An industrial firewall is a security device designed specifically for industrial control systems (ICS) and critical infrastructure (such as electricity, oil, and manufacturing) to protect industrial networks (OT networks) from cyberattacks. Unlike traditional IT firewalls, industrial firewalls need to adapt to the Ethernet physical environment and support industrial communication protocols (such as Modbus, PROFINET, DNP3, etc.).
Core features of industrial firewalls
1. Industrial protocol support
● Deep analysis of industrial control protocols (such as OPC UA, S7Comm), detection of malicious instructions (such as illegal PLC write operations).
2. High reliability
● Wide temperature design (-40℃~70℃), anti-electromagnetic interference (EMC), adaptable to environments such as factories and substations.
3. Low latency
● Avoid real-time control (such as robots and PLC communications) affected by security checks.
4. OT/IT fusion protection
● Protects both industrial equipment (such as SCADA, PLC) and IT networks (such as corporate office networks) from threat penetration.
Typical application scenarios of industrial firewalls
●Smart factory: protecting production line equipment (such as industrial robots, CNC machine tools).
●Energy industry: power grid SCADA system, oil pipeline control network.
●Transportation system: rail transit signal control, airport baggage sorting system.
How to use industrial firewalls?
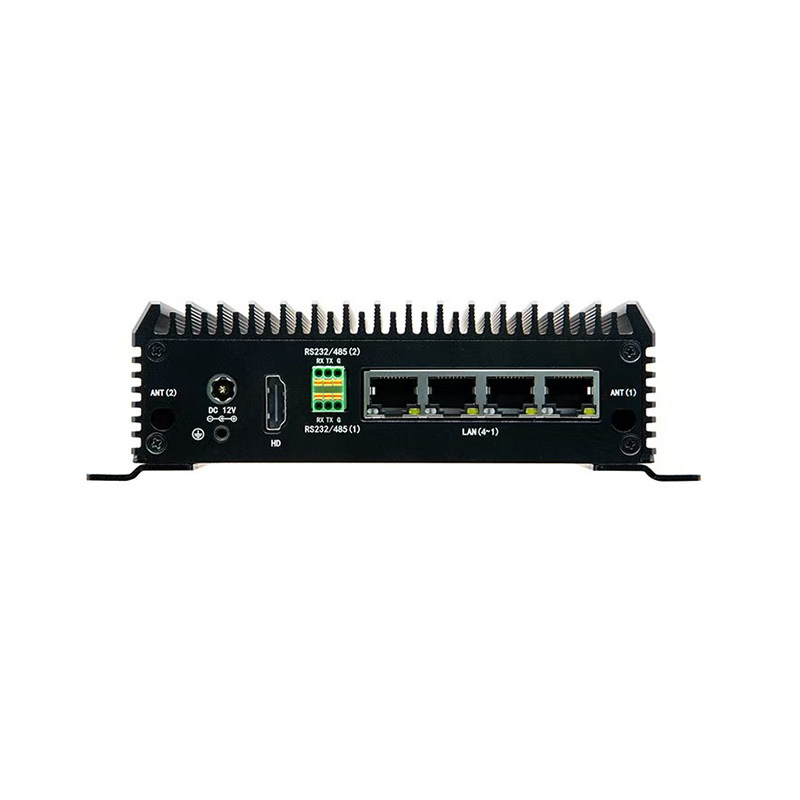
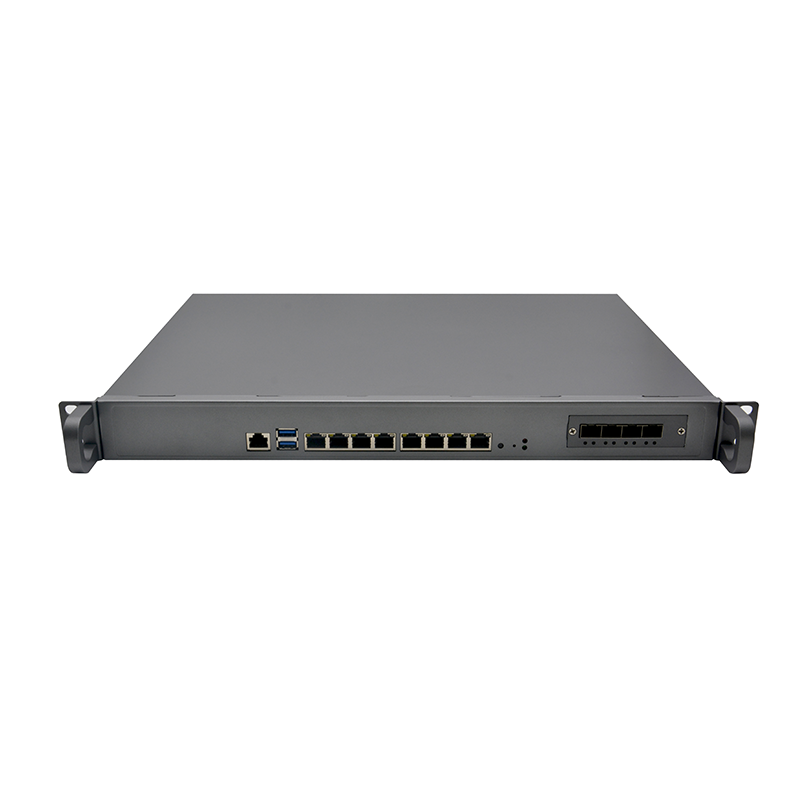
1. Deployment location
●Industrial firewalls are usually deployed at the following key nodes:
●The boundary between OT and IT networks (such as between the enterprise office network and the industrial control network).
●Between the control layer and the device layer (such as the SCADA server and PLC/RTU).
2. Configuration steps
(1) Basic access control
● Whitelist mode: Only allow necessary communications (such as Modbus TCP port 502).
● Disable default rules: Disable the ANY→ANY policy to avoid opening high-risk ports (such as Telnet 23).
(2) Industrial protocol deep detection
● Identify abnormal instructions (such as PLC stop commands sent by unauthorized devices).
● Support protocols: Modbus, PROFINET, DNP3, OPC UA, etc.
(3) Logs and alarms
● Send logs to SIEM systems (such as Splunk, Industrial SOC).
● Set real-time alarms (such as abnormal PROFINET traffic detected).
3. Advanced function configuration
● Intrusion prevention (IPS): Block attacks against industrial control vulnerabilities (such as CVE-2015-5374 Siemens PLC vulnerability).
● VPN encryption: Protect remote maintenance channels (such as IPsec VPN access to PLC).
● Traffic baseline learning: Automatically identify normal communication modes and issue alarms when they deviate.
4. Management and maintenance
● Regular audit rules: Clean up redundant policies and optimize performance.
● Firmware upgrade: Patch the firewall‘s own vulnerabilities (such as CVE-2023-XXXX).
● Backup configuration: Prevent device failure from causing policy loss.
Industrial Firewall vs. Traditional IT Firewall
| Comparison Item | Industrial Firewall | Traditional IT Firewall |
| Protocol support | Modbus, PROFINET and other industrial control protocols | HTTP, FTP and other IT protocols |
| Environmental adaptability | High temperature resistance, dust resistance, and electromagnetic interference resistance | Usually used in computer rooms or office environments |
| Real-time requirements | Low latency (millisecond level) | Can tolerate higher latency |
| Management interface | Simplifies operation and adapts to the habits of OT personnel | Designed for IT administrators |
Best Practices
1. Principle of least privilege: Only open necessary ports and protocols.
2. Physical isolation supplement: Combined with one-way network gate (Data Diode), reverse penetration is completely blocked.
3. Personnel training: Industrial control operation and maintenance personnel need to master firewall policy management to avoid "all release".
4. Compliance: Comply with IEC 62443, MLSA 2.0 and other standards.
Common Problems and Solutions
●Problem 1: Firewall causes PLC communication delay?
Solution: Adjust the detection strategy or enable "fast path" mode.
●Problem 2: Mistakenly intercept legitimate industrial control protocols?
Solution: Use Wireshark to capture packets for analysis and adjust the protocol whitelist.
●Problem 3: Firewall itself is attacked?
Solution: Close the remote management interface and enable MFA authentication.


















 Teamas
Teamas